Infographic Cloud Native Vs Enables Apps 724x1024
What is Cloud Native Applications?
By Pivotal’s definition, Cloud native is an approach to building and running applications that fully exploit the advantages of the cloud computing model.” In simple words a cloud-native (or cloud-based) application is the one which is created in the cloud and is built as microservices packaged in containers.
What are the benefits of Cloud Native Applications?
One of the huge advantages of cloud native is that it entails adopting open source software as the infrastructure and so that open-source software helps avoid lock-in. Kubernetes and other cloud native technologies work great for private cloud, public cloud and hybrid cloud. You can burst your capacity in the public cloud even if the base is in your own private cloud.
The key part of the cloud native architecture is this insistence on continuous integration and continuous deployment. Your infrastructure is programmatic as a concept of infrastructure as code. Once you make the investment, the lift-and-shift migration model to bring legacy systems from data centers to the cloud carries benefits like increasing redundancy and lowering costs.
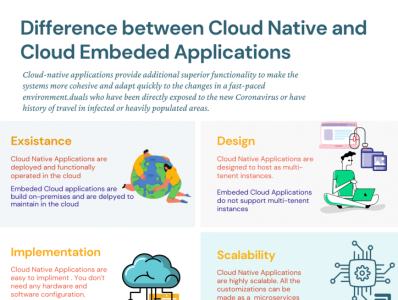
What is the difference between Cloud Native Applications and Cloud Embeded Applications?
Cloud-native edge provides a rich understanding of operations through environmental data that can provide deep insights into current operations. You can figure out the possibility of improvement over time with automation. It enables to scale the operations to millions of endpoints. Here is the key difference between them.
Cloud Native Applications are the future
If you are thinking about IoT/AL/ML robots, chat bots and other predictive maintenance in factories, you need a special force to shift to a more distributed infrastructure. Cloud Native Applications can help you in massively scalable IoT, and possibly even new business models. It also supports the equipment-as-a-service (EaaS) sector. .